Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Onutai, S.; Sato, Junya; Osugi, Takeshi
Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 319, p.123808_1 - 123808_10, 2023/03
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:84.39(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Onutai, S.; Osugi, Takeshi; Sone, Tomoyuki
Materials, 16(3), p.985_1 - 985_14, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:87.83(Chemistry, Physical)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Hokkaido University*
JAEA-Review 2022-050, 116 Pages, 2023/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Safe, efficient cementation of challenging radioactive wastes using alkali activated materials with high-flowability and high-anion retention capacity" conducted from FY2019 to FY2021. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to explore alkali activated materials with high anionic nuclide retention and flowability and their recipes for safe storage and disposal of iron flocculant from the water treatment facility at 1F, and to propose a design of a solidification device that is feasible as an actual plant. In order to achieve these objectives, the following five items were carried out in this study.
Reeb, C.*; Davy, C. A.*; Pierlot, C.*; Bertin, M.*; Cantarel, V.; Lambertin, D.*
Cement and Concrete Research, 162, p.106963_1 - 106963_16, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:56.94(Construction & Building Technology)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Hokkaido University*
JAEA-Review 2021-036, 95 Pages, 2021/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Safe, efficient cementation of challenging radioactive wastes using alkali activated materials with high-flowability and high-anion retention capacity" conducted in FY2020. For safe storage and disposal of iron sludge generated from contaminated water treatment, the present study aims to 1) explore alkali activated materials (AAM) with high-flowability and high-anion retention capacity and its recipe, 2) try mock-up manufacture and evaluation for one-tenth the size of real waste and propose the concept of the manufacturing equipment for a real plant, 3) show potential of AAM as the material for the solidification of waste with various physicochemical properties and radioactive nuclide compositions from the result ...
Kawaguchi, Munemichi
Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 125(22), p.11813 - 11819, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:13.34(Chemistry, Physical)Isothermal and constant heating thermogravimetry-differential thermal analysis (TG-DTA) and Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR) measurements have been performed for pre- and post-fired sodium hydride (NaH) in the temperature range of 500-700 K, respectively. Temperature dependence of NaH thermal decomposition rates obtained by the isothermal TGs showed an inflection point at around 620 K, which was caused by two kinds of hydrogen states (rapid diffusing and immobile hydrogen). In the FTIR spectra for the NaH and sodium (Na), the specific signals were observed at around 873.4, 1010.4, 1049.5 and 1125.7 cm , and the integrated values of FTIR signals for post-fired NaH at below 550K and at above 698 K were comparable to those for pre-fired NaH and Na, respectively. Those for post-fired NaH at 602-667 K were the intermediate values of the pre-fired NaH and Na, which denoted that the Na-Na bonds haven't grown sufficiently and the hydrogen coexisted in metallic Na. In order to predict the practical kinetics of NaH thermal decomposition reaction, we suggested the simple kinetics model which assumed two kinds of rapidly diffusing and immobile hydrogen states. The simulation results revealed the inflection point in temperature dependence of the thermal decomposition rates accordingly because the transition from immobile hydrogen to rapid diffusing hydrogen crosses over at around 620 K.
, and the integrated values of FTIR signals for post-fired NaH at below 550K and at above 698 K were comparable to those for pre-fired NaH and Na, respectively. Those for post-fired NaH at 602-667 K were the intermediate values of the pre-fired NaH and Na, which denoted that the Na-Na bonds haven't grown sufficiently and the hydrogen coexisted in metallic Na. In order to predict the practical kinetics of NaH thermal decomposition reaction, we suggested the simple kinetics model which assumed two kinds of rapidly diffusing and immobile hydrogen states. The simulation results revealed the inflection point in temperature dependence of the thermal decomposition rates accordingly because the transition from immobile hydrogen to rapid diffusing hydrogen crosses over at around 620 K.
Bateman, K.; Amano, Yuki; Kubota, Mitsuru*; Ouchi, Yuji*; Tachi, Yukio
Minerals (Internet), 11(6), p.588_1 - 588_19, 2021/06
Times Cited Count:4 Percentile:43.25(Geochemistry & Geophysics)Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Hokkaido University*
JAEA-Review 2020-054, 72 Pages, 2021/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2019. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Safe, efficient cementation of challenging radioactive wastes using alkali activated materials with high-flowability and high-anion retention capacity". The purpose of this study is to find safe, efficient cementation of challenging radioactive wastes using alkali activated materials with high-flowability and high-anion retention capacity, and to propose the concept of a manufacturing apparatus that is established as an actual plant. As a result of study in this year, it was revealed that the K-based alkali activated material has high-flowability and quick curing, and that high-iodine retention capacity is achieved by incorporating silver ions during manufacturing of solidified waste.
Sugiura, Yuki; Ishidera, Takamitsu; Tachi, Yukio
Applied Clay Science, 200, p.105910_1 - 105910_10, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:56.97(Chemistry, Physical) O-2SiO
O-2SiO , Na
, Na O-2SiO
O-2SiO and K
and K O-2SiO
O-2SiO
Kawaguchi, Munemichi; Uno, Masayoshi*
Journal of the Ceramic Society of Japan, 128(10), p.832 - 838, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:16.44(Materials Science, Ceramics)This study developed phase-field method (PFM) technique in oxide melt system by using a new mobility coefficient ( ). The crystal growth rates (
). The crystal growth rates (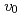 ) obtained by the PFM calculation with the constant
) obtained by the PFM calculation with the constant  were comparable to the thermodynamic driving force in normal growth model. The temperature dependence of the
were comparable to the thermodynamic driving force in normal growth model. The temperature dependence of the  was determined from the experimental crystal growth rates and the
was determined from the experimental crystal growth rates and the 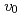 . Using the determined
. Using the determined  , the crystal growth rates (
, the crystal growth rates ( ) in alkali disilicate glasses, Li
) in alkali disilicate glasses, Li O-2SiO
O-2SiO , Na
, Na O-2SiO
O-2SiO and K
and K O-2SiO
O-2SiO were simulated. The temperature dependence of the
were simulated. The temperature dependence of the  was qualitatively and quantitatively so similar that the PFM calculation results demonstrated the validity of the
was qualitatively and quantitatively so similar that the PFM calculation results demonstrated the validity of the  . Especially, the
. Especially, the  obtained by the PFM calculation appeared the rapid increase just below the thermodynamic melting point (
obtained by the PFM calculation appeared the rapid increase just below the thermodynamic melting point (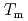 ) and the steep peak at around
) and the steep peak at around 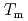 -100 K. Additionally, as the temperature decreased, the
-100 K. Additionally, as the temperature decreased, the  apparently approached zero ms
apparently approached zero ms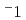 , which is limited by the
, which is limited by the  representing the interface jump process. Furthermore, we implemented the PFM calculation for the variation of the parameter
representing the interface jump process. Furthermore, we implemented the PFM calculation for the variation of the parameter  in the
in the  . As the
. As the  increased from zero to two, the peak of the
increased from zero to two, the peak of the  became steeper and the peak temperature of the
became steeper and the peak temperature of the  shifted to the high temperature side. The parameters
shifted to the high temperature side. The parameters  and
and  in the
in the  increased exponentially and decreased linearly as the atomic number of the alkali metal increased due to the ionic potential, respectively. This calculation revealed that the
increased exponentially and decreased linearly as the atomic number of the alkali metal increased due to the ionic potential, respectively. This calculation revealed that the  and
and  in the
in the  were close and reasonable for each other.
were close and reasonable for each other.
Nakayama, Masashi
JAEA-Data/Code 2020-009, 98 Pages, 2020/09
Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed a low alkaline cement, named as HFSC (Highly Fly-ash contained Silicafume Cement), in order to decrease the effect on geological environment of cementitious material. HFSC was used experimentally as the shotcrete (140m, 250m and 350m depth gallery) and lining concrete (GL-374m to GL-380m of east access shaft) in construction part of Horonobe URL. In order to evaluate the effect of HFSC on the surrounding rock and groundwater, concrete and rock cores were periodically sampled from the site where the in-situ construction test was conducted, and various analyzes were conducted. Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) was used for part of 140m depth gallery, and the same analysis as HFSC was conducted, in order to compare the effect of OPC and HFSC. This report summarizes the results of analyzes conducted on core samples from 2009 to 2018.
Sato, Junya; Shiota, Kenji*; Takaoka, Masaki*
Journal of Hazardous Materials, 385, p.121109_1 - 121109_9, 2020/03
Times Cited Count:9 Percentile:42.38(Engineering, Environmental)Lead is a hazardous heavy metal that can be stabilized by incorporation into the matrix of aluminosilicate bearing phases as they solidify. The actual mechanism by which lead is stabilized, however, continues to be unclear because the individual mechanisms of Pb incorporation into crystalline and amorphous aluminosilicate phases have not yet been studied separately. A detailed investigation of the incorporation of Pb into the amorphous phase of aluminosilicate solids was therefore performed. Amorphous aluminosilicate solids were synthesized with 0.7, 1.5, and 3.7 wt% of Pb from aluminosilicate gel produced from chemical reagents. Based on Raman spectroscopy, the Si-O stretching vibration bond shifted to lower wavenumbers with increasing Pb concentration. This shift suggested that covalent bonding between Pb and O in the matrix of the aluminosilicate solids increased. In addition, sequential extraction revealed that most of the Pb (75-90%) in the aluminosilicate solids was in a poorly soluble form (i.e. reducible, oxidizable, and residual fractions). These findings indicate that most of Pb is bonded covalently to the amorphous phase in aluminosilicate solids.
Nakayama, Masashi; Niunoya, Sumio*; Miura, Norihiko*; Takeda, Nobufumi*
JAEA-Research 2017-016, 62 Pages, 2018/01
The Horonobe URL Project has being pursued by JAEA to enhance the reliability of relevant disposal technologies through investigations of the deep geological environment within the host sedimentary formation at Horonobe, Hokkaido. The URL Project consists of 2 major research areas, "Geoscientific Research" and "Research and Development on Geological Disposal Technologies", and proceeds in 3 overlapping phases, over a period of around 20 years. Phase III (Investigations in the underground facilities) investigation was started in 2010 FY. The in-situ experiment for performance confirmation of engineered barrier system (EBS experiment) had started 2013 at GL-350 m gallery, and heating by electric heater in simulated overpack had started in January, 2015. One of objectives of the EBS experiment is acquiring data concerned with THMC coupled behavior. These data will be used in order to confirm the performance of engineered barrier system. This report shows consideration of concrete-type plug composition. The low alkaline cement developed by JAEA, called HFSC, was used for the plug. HFSC has used in construction test at the gallery as shotcrete in Horonobe URL.
Nakayama, Masashi; Niunoya, Sumio*; Minamide, Masashi*
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 23(1), p.25 - 30, 2016/06
In Japan, any high-level radioactive waste repository is to be constructed at over 300m depth below surface. Tunnel support is used for safety during the construction and operation, and shotcrete and concrete lining are used as the tunnel support. Concrete is a composite material comprised of aggregate, cement and various additives. Low alkaline cement has been developed for the long term stability of the barrier systems whose performance could be negatively affected by highly alkaline conditions arising due to cement used in a repository. Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has developed a low alkaline cement, named as HFSC (Highly fly-ash contained silicafume cement), containing over 60wt% of silica-fume (SF) and coal ash (FA). JAEA is presently constructing an underground research laboratory (URL) at Horonobe for research and development in the geosciences and repository engineering technology. HFSC was used experimentally as the shotcrete material in construction of part of the 350m deep gallery in Horonobe URL in 2013. The objective of this experiment was to assess the performance of HFSC shotcrete in terms of mechanics, workability, durability, and so on. HFSC used in this experiment is composed of 40wt% OPC (Ordinary Portland Cement), 20wt% SF, and 40wt% FA. This composition was determined based on mechanical testing of various mixes of the above components. Because of the low OPC content, the strength of HFSC tends to be lower than that of OPC in normal concrete. The total length of tunnel constructed using HFSC shotcrete is about 112m at 350m deep drift. The workability of HFSC shotcrete was confirmed by this experimental construction. In this report, we present detailed results of the in-situ construction test.
 activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditions
activity and temperature on the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite under highly alkaline conditionsSawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Mukai, Masayuki
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.267 - 278, 2016/05
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.23(Chemistry, Physical)The dependences of the dissolution rate of compacted montmorillonite on activity of OH (a
(a -) and temperature (T) were investigated. The dissolution rate of montmorillonite (
-) and temperature (T) were investigated. The dissolution rate of montmorillonite (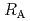 ) in compacted pure montmorillonite, which was formulized as
) in compacted pure montmorillonite, which was formulized as 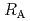 = 10
= 10 (a
(a -)
-)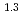 e
e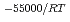 , was higher than that in the compacted sand-bentonite mixtures:
, was higher than that in the compacted sand-bentonite mixtures: 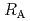 = 3500 (a
= 3500 (a -)
-)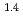 e
e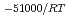 . The difference can be explained by considering the decrease in a
. The difference can be explained by considering the decrease in a - in the mixtures accompanied by dissolution of accessory minerals such as quartz and chalcedony. The dissolution rate model developed for pure montmorillonite is expected to be applied to bentonite mixtures if quantification of the decrease in a
- in the mixtures accompanied by dissolution of accessory minerals such as quartz and chalcedony. The dissolution rate model developed for pure montmorillonite is expected to be applied to bentonite mixtures if quantification of the decrease in a - is achieved somehow.
- is achieved somehow.
Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Sawaguchi, Takuma; Tsukada, Manabu; Hoshino, Seiichi*; Tanaka, Tadao
Clay Minerals, 51(2), p.279 - 287, 2016/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:24.23(Chemistry, Physical)Alteration of bentonite-cement interfaces and accompanying changes in diffusivity of tritiated water was experimentally investigated using intact hardened cement specimens. The alteration by carbonate solution was accompanied by mineralogical changes at the interface and a decrease in the diffusivity to 70% of the initial value after 180-day period. Another alteration under silicate system contacting hardened cement and compacted bentonite was accompanied by mineralogical changes at the interface and a decrease in the diffusivity to 71% of the initial value after 600-day period. The changes in the diffusivity were much less than those observed for mixed specimens of granulated hardened cement and bentonite where the diffusivity decreased down to 20% of the initial value over 180 days. The results were extrapolated to 15 years under simple assumptions and showed good agreement with those observed in the cement-argillite interface at Tournemire URL. Such an explanation enhances our confidence in our assessment of alteration of cement-bentonite systems and can be a base for using our data and models in long term assessment of radioactive waste disposal.
Ikeda, Takashi; Boero, M.*
Journal of Chemical Physics, 143(19), p.194510_1 - 194510_7, 2015/11
Times Cited Count:30 Percentile:76.81(Chemistry, Physical)By resorting to a novel implementation of the first-principles-based van der Waals correction based on maximally localized Wannier functions, we inspect its performance and assess its reliability for aqueous solutions of alkali metal ions. We find that van der Waals interactions, when added to the widely used revPBE gradient corrected functional, influence substantially both structural and dynamical properties of water molecules, with particular emphasis on the hydration shell of the alkali cations. These effects are more evident for strong structure-making and -breaking cationic species. Moreover, self-diffusion coefficients and reorientation correlation times of solvating water molecules change systematically, showing a trend in better agreement with experiments with respect to simulations neglecting the long-range dispersion contributions.
Baba, Yuji; Shimoyama, Iwao; Hirao, Norie; Izumi, Toshinori
e-Journal of Surface Science and Nanotechnology (Internet), 13, p.417 - 421, 2015/09
Times Cited Count:1The interaction between alkali metals and oxides has attracted much attention as heterogeneous catalysis, chemical reaction promoters, and high intensity electron emitter. Also the interaction of cesium and oxides has become important subject, because radioactive cesium trapped in minerals such as clay and soil may cause health risks. In the present study, we analyzed chemical states of ultra-trace amount of cesium on oxide surfaces by total reflection X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (TR-XPS) exited by synchrotron radiation. For the adsorbed cesium thicker than 0.01 layer, cesium is weakly bound with oxide through Van-der-Waals force. On the other hand, for ultra-thin layer about 0.002 layer, the chemical bond changes to covalent bond. It is suggested that this change in the chemical bonding state is one of the reasons why radioactive cesium is hard to be released from minerals.
 AV1934, a classic alkaliphile isolated from human feces in 1934
AV1934, a classic alkaliphile isolated from human feces in 1934Attie, O.*; Jayaprakash, A.*; Shah, H.*; Paulsen, I. T.*; Morino, Masato*; Takahashi, Yuka*; Narumi, Issey*; Sachidanandam, R.*; Sato, Katsuya; Ito, Masahiro*; et al.
Genome Announcements (Internet), 2(6), p.e01175-14_1 - e01175-14_2, 2014/11
 sp. strain TS-2, isolated from a jumping spider
sp. strain TS-2, isolated from a jumping spiderFujinami, Shun*; Takeda, Kiyoko*; Onodera, Takefumi*; Sato, Katsuya; Sano, Motohiko*; Narumi, Issey*; Ito, Masahiro*
Genome Announcements (Internet), 2(3), p.e00458-14_1 - e00458-14_2, 2014/05